LIVER DISEASES
Normal Anatomy and Physiology
NOTES
- liver lobules have tiny triads at each node of the hexagon
- liver divided up into zones from the outer blood supply --> inward toward the terminal hepatic vein (Z1, Z2, Z3)
- Z3 most susceptible to necrosis
Main Function: - metabolize products using enzymes, store them and send to periphery targets
- disease from decreased metabolism & accumulation of:
--> iron, copper, fat
Liver Regeneration
- hepatocytes very good at regenerating
- can regenerate if 7/8 of liver destroyed
Liver Necrosis & Apoptosis
- "councilmen bodies" = apoptosis of single hepatocytes
Liver Fibrosis
- main change in liver that leads to poor perfusion and liver cirrhosis
- collagen laid down by stellate cells and hepatocytes stop functioning properly
--> fibrotic collagen stops perfusion to zone 3 --> spreads
Liver Disease
--> diagnosed as either
acute or chronic
Liver Responses to Disease States
Hepatic *Encephalopathy
- Flapping tremour = astirixis
Signs and Symptoms
- confusion
- memory loss
- change in mood
- Flapping tremour = astirixis
Overt vs. Minimal
- 50% of people with cirrhosis will have Overt
--> Overt display these symptoms
--> minimal do not display these symptoms
Regeneration
- can regenerate even when
7/8 of hepatocytes lost
Inflammation
Necrosis and Apoptosis
- used to get rid of infected/compramised hepatocytes
- apoptosis of individual hepatocytes:
--> develop councilman bodies
Fibrosis
- response to chronic inflammation and stress on hepatocytes
--> stellate cells in Space of Disse
--> lay down excessive collagen for fibrosis
--> hepatocytes have harder time to absorb and secrete into the sinusoids
Intracellular Accumulation in Hepatocytes
- Hepatocytes diverted from normal functions
--> due to fighting disease, toxins, etc. - accumulation of products
--> lipotoxicity (fatty liver disease)
--> copper ions (Wilson's disease & K-F rings)
--> Iron ferrous ions (Hemochromatosis)
Liver Function Tests and Ezymes
Liver Enzymes
AST and ALT
- raised ALT and AST very
non-specific marker of liver
disease of any kind - higher AST to ALT ratio
--> specific to alcoholic liver disease
Acute Liver Disease
- does NOT require a biopsy for diagnosis
Jaundice
- yellowing of the skin, sclera, conjunctiva
- raised bilirubin
--> > 40 micromol/L - note usually get jaundice in acute liver disease and less common in chronic liver diseases
Bilirubin
- breakdown product of Heme from RBCs sent to the liver
- Heme broken down to Fe2+ and bilirubin
Unconjugated Bilirubin
- hydrophobic = NOT water-soluble
- requires albumin for transport in the blood
Conjugated Bilirubin
- hydrophilic = water-soluble
- conjugated in the liver by glucoronic acid
Classification of Jaundice
Build up of UNCONJUGATED bilirubin
Unconjugated
Hyperbilirubinemia
Pre-Hepatic Jaundice
Causes
- outside of liver production of unconjugated bilirubin
- hemolytic diseases (breaking of heme from RBCs)
Hemolytic Anemias
- ex: Sickle Cell Disease
Parasitic and Viral
- Pre-Hepatic Malaria (parasite)
- infect RBCs and destroy Heme proteins
Build up of CONJUGATED bilirubin
+++ Build up of CONJUGATED bilirubin
Post-Hepatic
Causes
- Gallstone choledocholithiasis
- carcinoma of head of pancreas
--> blocks the bile duct
Signs and Symptoms
- dark urine
--> conjugated bilirubin in the urine
--> normally should ONLY have
urobilinogen in urine
CONJUGATED/UNCONJUGATED
bilirubin accumulation in the liver
Intra-Hepatic Jaundice
Causes
- failure of liver to conjugate bilirubin with glucoronic acid
--> unconjugated bilirubin accumulates in the liver
Liver Diseases
Newborns
- immature liver enzymes
cannot conjugate the bilirubin - babies don't make biliverdin until 4 days
*Chronic Liver Disease
- requires a biopsy for diagnosis
and classify as either grade 1 or 2
Common Causes
Most Common = Hepatitis A
- note Hep A is acute
and Hep C is chronic
Classification of
Chronic Liver Disease
Grade 1
- inflammatory cells ONLY
near the portal veins
Grade 2
- inflammatory cells
throughout parenchyma - parenchyma = the functional tissue of an organ as
distinguished from the connective and supporting tissue
Chronic Liver Disease
Outcomes
*Hepatic Failure
- liver stops functioning
- only happens when 7/8
of liver is non-functioning
due to chronic cirrhosis
--> cannot regenerate and survive
Chronic Liver
Disease Causes
50% Hepatitis C Viral Infection
- note Hep A is acute
and Hep C is chronic
25% Alcoholic Liver Disease
ACUTE Drug/Toxin Induced
- paracetamol overdose
HEPATITIS
- can be acute vs. chronic
- can be infectious vs. non-infectious
Classification:
- Infectious
- Non-infectios
Infectious
Hepatitis
Non-Infectious
Hepatitis
Viral Hepatitis Infections
- most common
- Hepatitis viral infections very good
at hiding from the immune system
--> not recognized and presented
on MHC1 receptors well
Parasites
- malaria
Signs and Symptoms
- hepatomegaly and tenderness on exam
- jaundice one week after onset
- nausia, anorexia, general malaise
Chronic Hepatitis Viruses (B,C,D)
- presents within months to years
- leads to all complications of chronic hepatitis
Acute Hepatitis Viruses (AFE)
- presents within weeks to months
- RARELY leads to liver failure
(though possible)
Bacteria
- staphylococcus, salmonella, TB
Classification:
- Acute
- Chronic
Acute
Hepatitis
Hepatomegaly
- swelling of hepatocytes
Bacteria
- staphylococcus, salmonella, TB
Chronic
Hepatitis
Most common = Hepatitis A Virus
Most commmon = Hepatitis C Virus
Hepatitis D Virus
Hepatitis B Virus
Very Rare
Acute Hep. Viruses
Hepatitis E Virus
Hepatitis F Virus
Treatment
Notes
- Hep B and D more severe acute conditions
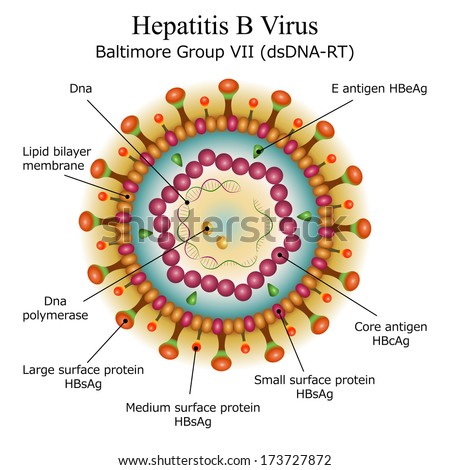
than Hep A and Hep C - 3 key components that make it a good virus
--> outer envelope for protection and entry/exit into cells
--> middle capsid protection
--> ds DNA virus (no need for transcription) - long incubation period = 3 months
-2 targeted antigens for antibodies
--> Hep B core antigen = HBcAg
--> Hep B surface antigen = HBsAg
click to edit
click to edit
Risk Factors
- 1-10% indrug addicts
and hemopheliacs
click to edit
Notes
- ONLY possible
after Hep B Virus infection (carriers of Hep B)
--> or co-infection with Hep B - Hep B and D more severe acute conditions
than Hep A and Hep C
--> though less common than Hep A and C
Drug Addicts
Hemopheliacs
- get many blood trransfusion
click to edit
click to edit
Outcomes
- leads to all outcomes of general chronic liver disease
- see "chronic liver disease"
--> fibrosis, cirrhosis (nodule formation), etc.
Drug/Toxin Induced Liver Disease
*Alcoholic Liver Disease
- most common cause of liver cirrhosis
Pathophysiology
- needs to be constant and chronic alcoholism
- leads to irreversible changes in the:
--> anatomy, organization and blood perfusion
Key Features
- cirrhosis
--> MICRONODULAR specific to alcoholic liver disease
--> C2H5OH (ethanol) directly ups collagen fibrosis from stellate cells - serum AST higher than ALT (ratio>2)
--> distinct to alchoholic liver disease
--> remember Alcoholis have "asterixis" --> higher "AST"
- high serum levels of gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) - liver steatosis
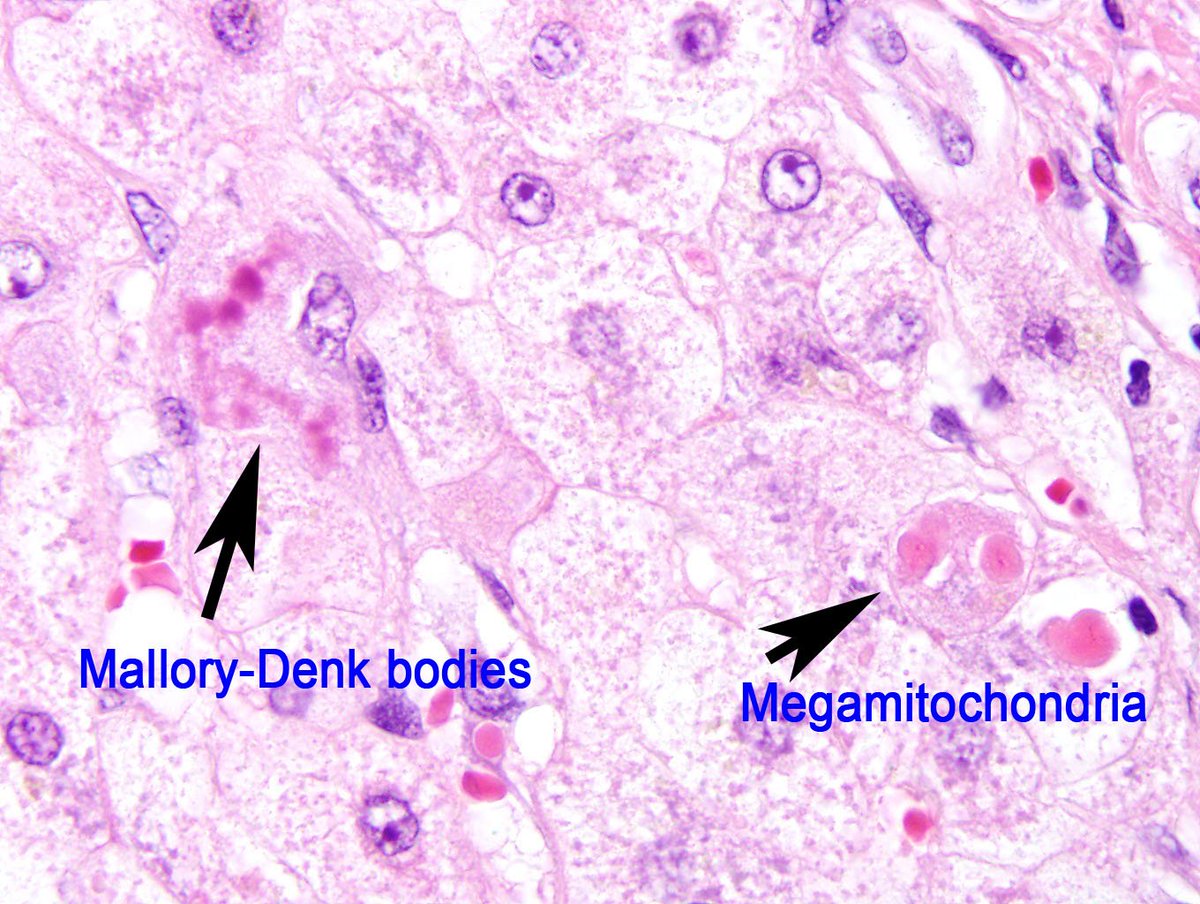
--> (fat deposits in the liver) - Mallory Bodies/Hyaline
--> damaged microfilaments in hepatocytes accumulate
--> tangled pink strands in hepatocytes
Signs and Symptoms
- encephalopathy
--> build up of ammonium
--> confusion - abdominal weight gain (of fat)
- portal hypertension
- jaundice
Paracetemol Overdose
*Autoimmune Liver Diseases / Biliary tract diseases
- 3 types
General Auto-immune Hepatitis
Treatment
- steroids
--> lowers inflammatory response
Risk Factors
- more common in women
Signs and Symptoms
- raised AST and ALT (general)
- raised alkaline phoshpatase (liver and bone general)
- raised IGg antibody levels
Metabolic/Genetic
Liver Diseases
α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
Cause
- leads to emphysema (COPD)
- alveolar specialized macrophages
--> release trypsin (protease) for
protection of alveoli from pathogens - α1-Antitrypsin
--> enzyme made by the liver
--> sent to the alveloar acinar cells
--> alveloar acinar cells use it to
protect themselves from trypsin
Outcomes
Emphysema and COPD
- destruction of the alveolar sac of the lungs
Cancer and Liver Tumors
Secondary Tumors
- almost always metastases from other organs
--> due to high blood flow from portal vein system
--> all visceral organs drain into the liver
Primary Tumors
- extremely rare
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- most common type of primary liver tumor
- usually on background of:
--> chronic hepatitis (Hep B and C)
--> cirrhosis - high incidence in Africa and China
- main definite marker
--> allpha-fetoprotein
--> think fetor hepaticus
--> feto means it arises from the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma Carcinoma
- most rare type of primary liver tumor
- adenocarcinoma of the bile ducts of the liver
5% Hepatitis B Viral Infection
10% Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
(NAFL Disease)
ALT = alanine transaminase
--> involved in Cahill Cycle
--> transport of alanine and ammonia NH3 from muscle to liver
--> ALT transfers C-skeleton from alanine to make pyruvate in liver
AST = Aspartate transaminase
--> AST transfers C-skeleton from aspartate to make oxaloacetate in liver = last product of Krebb's cycle
Notes
- generally not life-threatening
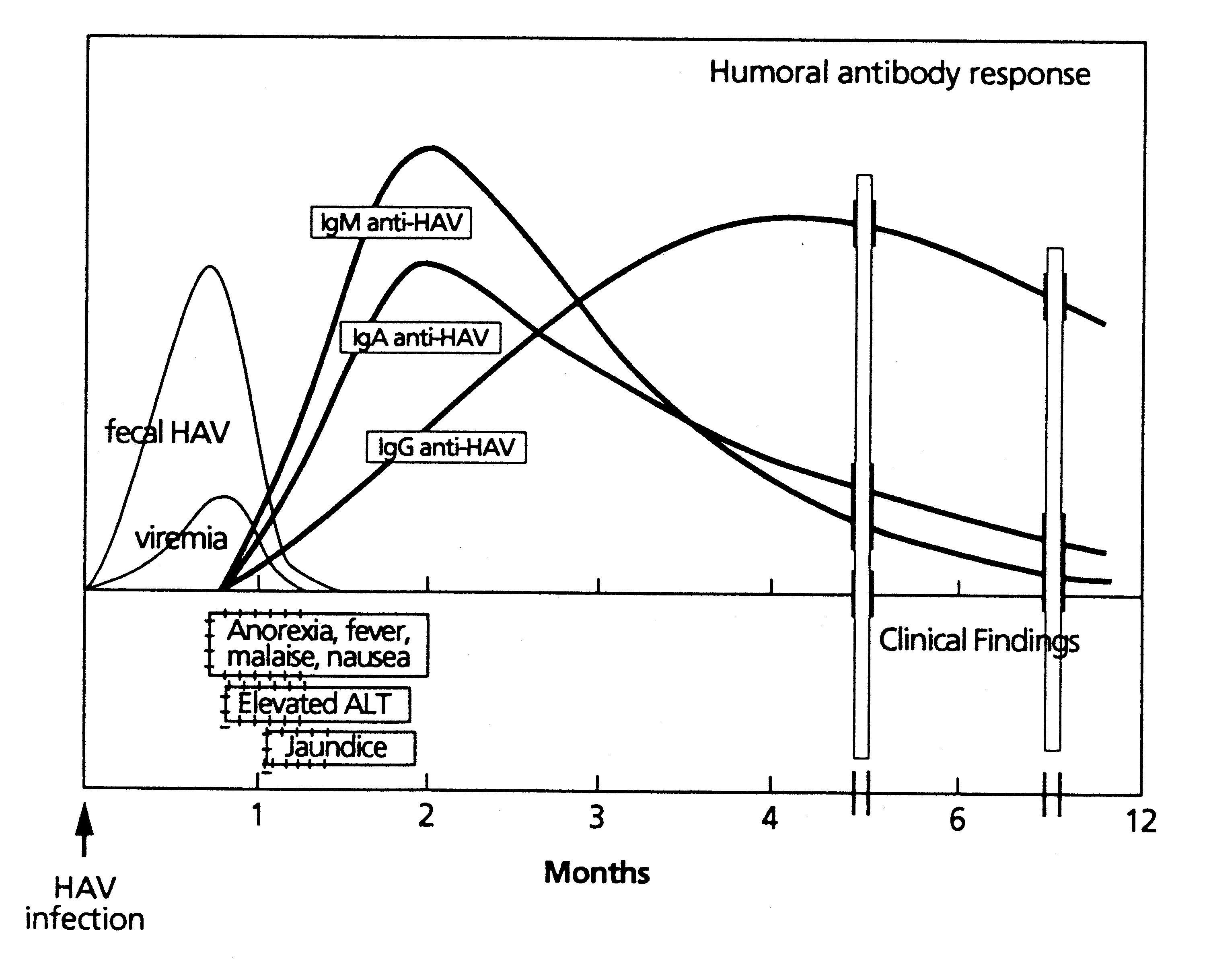
- develop IgM anti-HAV first
--> drop off at 3 months - develop IgG anti-HAV second
--> stay high even after 3 months
Spread
- mother to child
- sexually transmitted
Spread
- drug users
--> dirty needles - mother to child
- RARELY sexually transmitted
- anti-Rhesus D blood recipients in Ireland
Spread
- can infect pregnant women
click to edit
Liver Infections
Cause and Treatment
- build up of NAPQI
- less than 2 hrs.
--> treated with activated charcoal - more than 2 hrs.
--> glutathione from N-acetylcysteine
Alcohol Induced Hepatic Steatosis = *Fatty Liver Disease
- note can be caused by alcoholism and also idiopathic
- 2 main causes
- PRIMARY cause = lower beta hydroxy Lipolysis
--> FAs collect in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes - SECONDARY cause = NADPH excess by the 2 alcohol enzymes
--> alcohol DH = dehydrogenase
--> Aldehyde DH
Autosomal recessive *Hyperbilirubinemias
- Gilbert Syndrome
--> UDP - glucuronosyltransferase - Criglar-Najjar = milder form of Gilbert
- Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
*Dubin-Johnson Syndrome - Hyperbilirubinemias
- autosomal recessive
- Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
--> opposite to Gilbert and Criglar-Najjar where they can't conjugate bilirubin - Dubin can conjugate the bilirubin, but it CAN'T excrete it
--> collects in the liver = children with BLACK LIVER
--> black pigments
--> usually benign
*Gilbert Syndrome - Hyperbilirubinemias
- autosomal recessive
--> UDP - glucuronosyltransferase - actually pretty common
- benign and waxing and waving unconjugated high bilirubin
*Criglar-Najjar Syndrome - Hyperbilirubinemias
- autosomal recessive
- The CUGGLER from community can't CONJUGATE
- milder form of Gilbert syndrome
--> UDP - glucuronosyltransferase
Pathophysiology
- on background of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis
- due to build up of ammonium reaching the brain
- astrocytes are the gatekeepers in 2 ways
--> seal off the Blood BB and only allow in certain things
--> recycle Glutamate from the synapses to make sure there is not too much glutamine in the synapses - GLUTAMATE = MAKES the neurons work
--> glutamine in inactive as a NT - Ammonia + glutamate = glutamine
--> glutamine released from astrocytes to the Neurons
--> glutaminase makes glutamine = NT
Treatment: Lactulose
- DOUBLE TREATMENT
- Lactulose = increased conversion ammonia --> ammonium
--> we can't absorb lactulose, but bacteria can
--> increased bacterial lactulose metabolism
--> increases OH production
--> OH traps NH3 into NH4 - rifaximin = decreases bacteria ammonia NH4 production
--> added onto lactulose - Lactulose is a PAD = poorly absorbed dissacharide
- reaches the colon unchanged
- want to trap Ammonia in the GI lumen
--> Only ammonia = NH3 crosses the intestine wall
--> NH3 combines with water to make NH4 and OH-
--> use osmotic laxitive to bring water into the lumen
--> H2O combines with NH3 to make NH4
--> traps it in the lumen for excretion
Secondary Treatment: Rifaximin
- antibiotic that kills gut bacteria that produce ammonia
Lactulose: Acidifying Agent for Encephalopathy
--> decreases the pH of the gut = acidifies the gut
--> H+ shifts ammonia and water equilibrium between the gut lumen and blood
--> H+ combines with hydroxide ion (that normally binds with ammonium to form ammonia in intra-gut ammonium equilibrium)
--> traps ammonium and water in the gut for excretion
--> trapping both the ammonia and water gives its 2 effects of laxative and anti-encaphalopathy
- anti-ammonia use --> given by enema or orally
Clinical Cases
Clinical Case
Notes:
- note that
Clinical Case
Encephalopathy Clinical Case
Case presentation:
Notes:
- Important to recognize the signs and symptoms of ecephalopathy and link it to pre-existing liver disease
--> hepatic flap
--> fetus hepaticus (ammonia breath --> sweet smelling)
--> confusion and seizures - hepatic encephalopathy usually comes after portal hypertension
- portal HTN is necessary since it brings toxins that are normally cleared by the liver and they are pushed back into circulation as the portal system goes back
- ammonia accumulates in the blood and eventually passes the blood BB
- necessary for lactulose to make acidic environment with extra protons H+ to bind with ammonia to trap it in the gut and excrete
--> fixes excess ammonia build up and hepatic encephalopathy
Liver *Abscesses
*Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension
*Portal Hypertension
Signs and Symptoms
Spider Naevi
Caput Medusae
- varicose and large veins
around the umbilicus - normal in pregnancy
Complications
Ascities
- fluid collection in abdomen
Splenomegaly
- enlargement of the spleen
- SMV and Splenic veins are the 2 main vein
that join to form the hepatic portal vein - direct back pressure to the Splenic vein
- also build up of toxins/pathogens in blood
that spleen must filter - danger of splenic rupture
Esophageal Varicose Veins
- back pressure to the splenic and left gastric vein
--> back pressure to lower esophageal vein branch - danger to rupture in esophagus
--> these veins have very thin walls - hematemesis
--> blood in the vomit
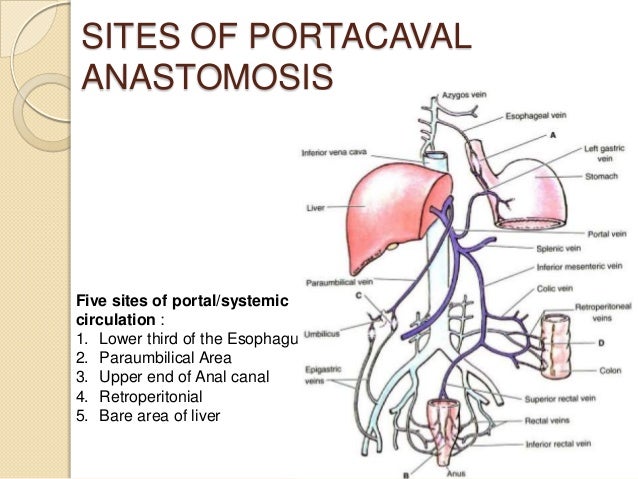
Portosystemic Anastamoses
- note that the portal vein system has no valves so the blood continues to back up until it reaches the connections of common draining sites with the systemic vein system
5 main areas of anastomoses:
- esophageal veins
- upper anal veins
- paraumbilical area
*Cirrhosis
Micro vs. Macro Nodular Cirrhosis
- micronodular = alcoholic liver disease
- macronodular = other liver diseases
Treatment
- Cirrhosis is IRREVERSIBLE
Definition
- regeneration of random/diffuse fibrotic NODULES in the liver
- disorganized liver anatomy
- blood has hard time reaching all areas
--> due to disorganization
Causes
- multiple causes
- most common = alcoholic liver disease
- only happens after chronic disease state and stress
Complications
Failure to make important proteins
- Albumin and
- Clotting Factors
Danger of Hemmorage
- low clotting factors
Constant Bruising and Bleeding
- low clotting factors
hypoabuminema
- systemic edema
Improper blood flow in liver
- liver stops functioning
- liver failure
Portal Hypertension
- see portal hypertension
Clinical Cases
Clinical Case
Notes:
- note that
Clinical Case
Case example:
Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension
Notes:
- solution to above = D the splenic vein since cirrhosis usually results in secondary portal hypertension which causes ascities and other sequalae (varicose veins, esophageal varices, etc.)
- portal veins system has no valves in it so when there is liver damage and inflammation that causes backup into the portal vein system, it keeps getting pushed further and further back
--> creating ascities and portal hypertension - pushes back eventually to the portosystemic anastomoses
--> here it hits the first valves of the systemic vein system and creates high pressure - common sites of potosystemic anastomoses:
--> esophageal varices
--> anal hemorroids
Cirrhosis Clinical Findings
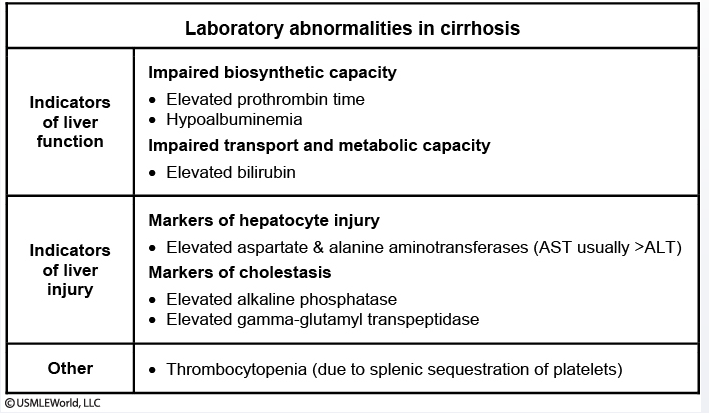
Lab Findings and Prognosis in Liver Cirrhosis
- dived between non-specific liver damage and biliary damage
- Non specific Liver markers:
--> release of intracellular hepatocyte and biliary contents
--> Hepatocytes = ALT and AST transaminases
--> biliary system = GGT and Alk Phosph - Cirrhosis specific Liver markers that lead to prognosis
--> low albumin
--> low PT = prothrombin time (extrinsic clotting factors)
--> bilirubin levels
Lactulose Primary Uses
- osmotic laxative normally used to treat constipation
--> increases cations in the gut
--> increases Cl- in the gut
--> Cl- brings water with it
--> increased flow/diarrhea - laxative use --> given orally
Cirrhosis Causing
Auto-Immune
Bile Duct Disorders
*PBC = Primary Biliary Cholangitis/Crrihosis
Defining Serum Tests
- high IgM antibodies
- high anti-mitochondrial antibodies
- high alkaline phosphatase
Causes and Defining Features
- cholangiohepatitis = slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver by immune cells
- PRIMARY BILIARY
--> antibodies attack primary start of biliary tree
--> caniculi of hepatocytes - PRIMARY BILIARY
--> very specific and primary to biliary tree only
--> no background of IBD like in Primary SCLEROSING cholangitis - results in cholestasis = causing bile and other toxins to build up in the liver
- +/- granulomas
Risk Factors
- more common in women than men
- NO association with IBD
*PSC = Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Causes and Defining Features
- progressive inflammatory destruction of post-hepatic biliary tree (ducts)
- Primary SCLEROSING
--> primarily causes sclerosis (scarring) of the entire biliary tree
--> sclerosis is very general widespread auto-immune
--> IBD background also
Risk Factors
- 2M : F
--> only auto-immune liver disease more common in men - 30-50 yrs old
- 70% have background of Ulcerative Colitis (sometimes CD)
*Wilsons and HEmochromatosis
- both are autosomal recessive genes
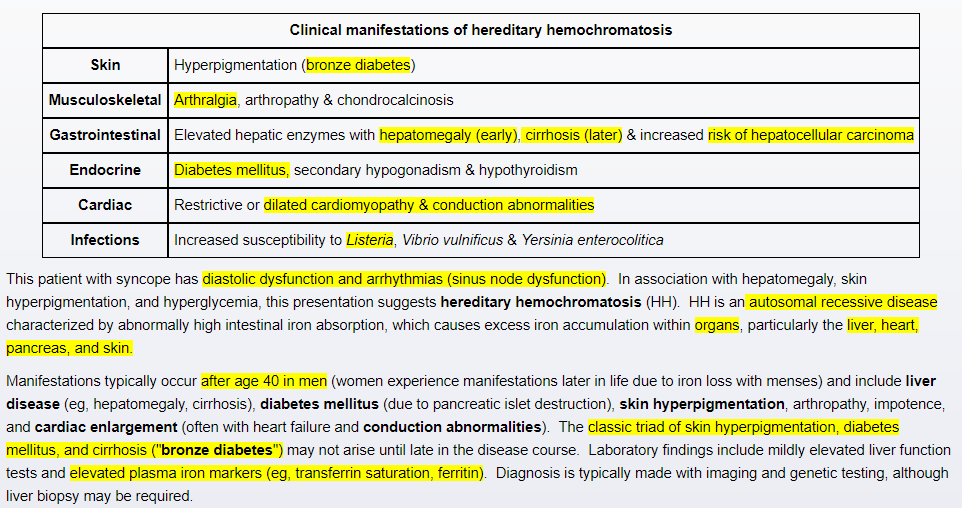
*Hemachromatosis
(a.k.a. = Bronze Diabetes)
Clinical presentation
- Iron gets deposited in different organs
Pancreas and Skin
--> "Bronze Diabetes"
Heart
--> cardiac failure
Liver
--> cirrhosis and liver failure
Pathophys and Iron Transport
- excessive absorption of iron (Fe2+)
from the small intestine - Autosomal recessive mutation
--> gene C282Y on chromosome 6
--> can't store iron properly (confirm?)
Clinical Cases
Hemachromatosis
Case Example
Notes:
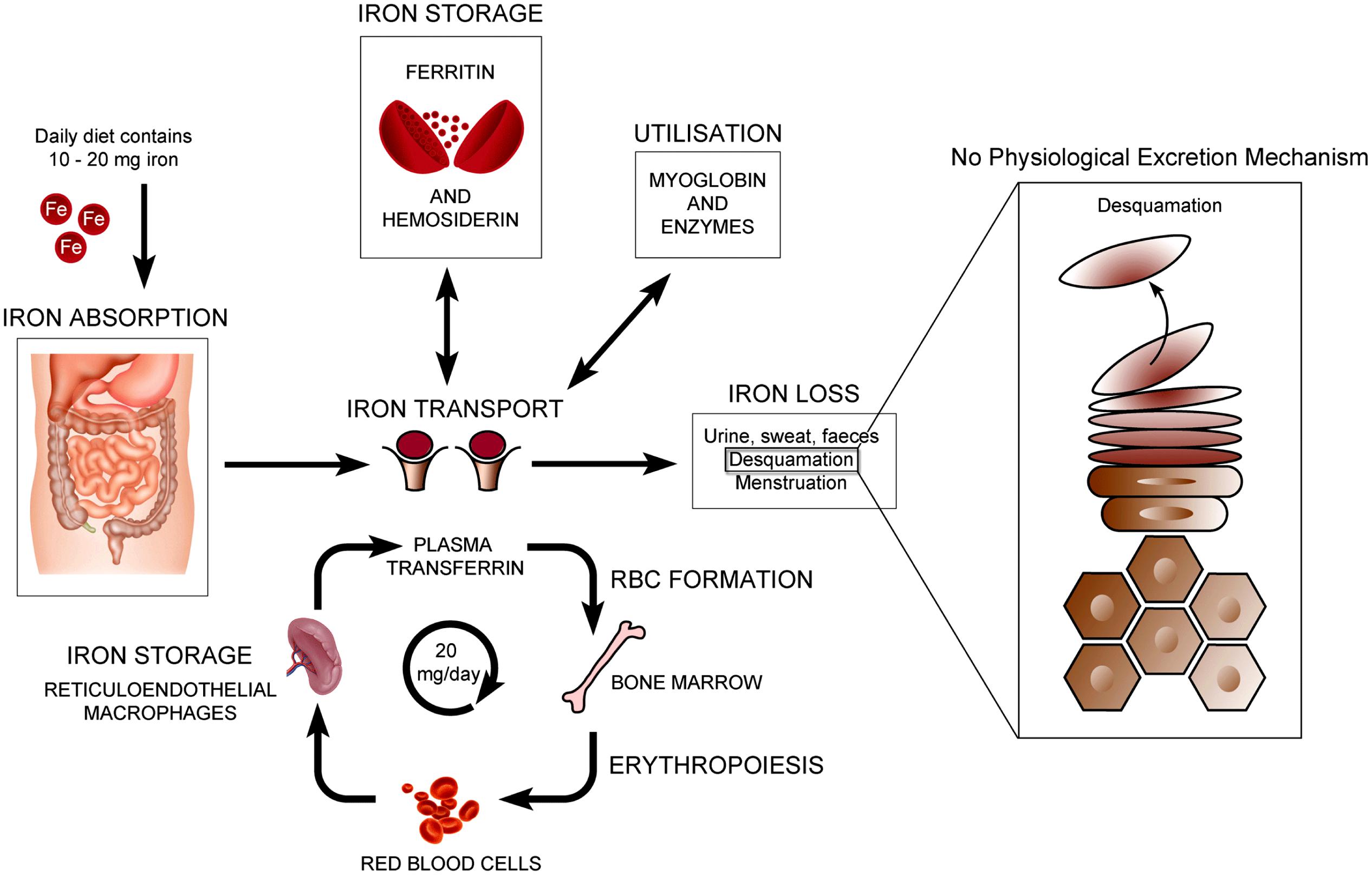
- note that iron is either stored as ferritin in tissues like the liver and in macrophages
--> or it is stored as hemosiderin, which is what gives pigment in the dermal layer of skin, as shown above
--> Bronze diabetes
*Wilson's Disease
- inherited parkinson's disease for the young (+ LFTs)
- present normally at a very young age in boys mostly
- note that Wilsons is NOT just a liver disease, it effects 3 main systems
--> liver, neurological and psychiatric - Neuro = hepatolenticulate disease
--> affects the Putamen and GPi and GPe of the lenticular nuclei
--> gait, parkinsonism - psych = can vary widely from personlity change to psychosis
- liver = chronic hepatitis
inherited parkinson's disease for the young (+ LFTs)
- Wilson's presents similar to PD
- gait disturbance
- tremors
- psychiatric (depression, mood changes, psychosis)
Outcomes
- copper gets deposited
in different organs
Pancreas and Skin
--> "Bronze Diabetes"
Keiser-Fletcher Rings
- brown ring of copper around the iris arcura in the eye
--> similar to blue arcura lipidosis rings from hyperlipidemia and hypercholestermia
--> reason for this is elastin content in the iris arcura (able to bind like FAs do in blood vessels)
Liver
--> cirrhosis and liver failure
Clinical Cases
Clinical Case
Notes:
- note that
Clinical Case
*Reye's Syndrome in Children
- caused by aspirin use in kids who have a current viral infection
- they have an underlying metabolism disorder for salycylates, but it is not activated until they have a virus (usually resp) that affects their liver
- 2 parts of Reyes syndrome
- Liver dysfunction - from the actual aspirin toxicity
--> note there is NO INFLAMMATION or necrosis in Reye's syndrome
--> there is ONLY steatosis of liver cells = fat collection - Hepatic Encephalopathy is the second stage of Reye's syndrome
*Slit lamp exam for Wilsons disease
- "WILSONS WILL SPLIT ON lamp exam"
- can detect Kayser Flescher rings you can't see on lcinical exam